Bus Topology Cable Type
Backbone Cable A backbone cable is nothing but a single cable that is used to connect all the network nodes to this cable so that bus topology will exist. Bus topology was used for early 10Base-2 ThinNet and 10Base-5 ThickNet coaxial cable Ethernet networks.

Topology Using Coaxial Cable Get Certified Get Ahead
1 It is easy to set-up and extend bus network.

. 4 Linear Bus network is mostly used in small networks. 2 Cable length required for this topology is the least compared to other networks. The main concepts covered in the bus topology mainly include backbone cable terminator drop link and node.
Ad Enjoy Fast Shipping Easy Returns On All Orders. 5 initially less expensive than other topologies. A bus topology is made up of the main cable that has a terminator at the end.
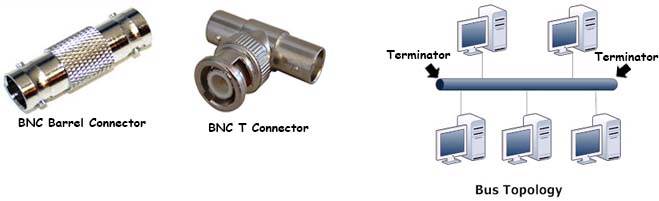
This single cable is commonly referred to as a backbone. The terminators are essential to allowing quality signal transference between the main cable and all devices within the network. A bus topology exists when all of the nodes on the network are connected to a single cable.
Spool size 16 AWG 18 AWG wire two conductors. Disadvantages Drawbacks of Linear Bus Topology. Its a submarine coaxial cable linking Japan Guam Havaii and mainland USA.
The fixed wiring methods shall be metal raceways nonmetallic raceways encased in not less than 2 inches of concrete. After that many transpacific submarine cable systems were built continuously. Fire alarm cables are also available with PVC insulation copper conductors.
348 Flexible Metal Conduit. The bus topology is designed in such a way that all the stations are connected through a single cable known as a backbone cable. Each node is either connected to the backbone cable by drop cable or directly connected to the backbone cable.
The first trans-Pacific submarine cable system TPC-1 Trans Pacific Cable 1 was put into servie on on June 19 1964. Fire alarm cables are available in various models sizes with 1000 ft. 340 Underground Feeder and Branch-Circuit Cable.
Via Hawaii with a small capacity of only 128 telephone lines. Types SE and USE. Nonmetallic-sheathed cable Type AC metal-clad cable and rigid nonmetallic conduit.
Terminators are fixed at both ends of the mainline wire. Depending on the type of computer network card a coaxial cable or an RJ. Stocking distributor of fire alarm cables.
Alternatively referred to as line topology bus topology is a network setup where each computer and network device is connected to a single cable or backbone. How many cables are needed. Definition Of A Bus Topology A bus topology is a type of local area network configuration in which computers or terminals also known as nodes are connected to a single cable as known as the backbone.
3 Bus topology costs very less. This article discusses some of the reasons why a bus topology requires terminators in its structural framework. Bus topology is also called backbone topology or line topology.
Types NM NMC and NMS 336 Power and Control Tray Cable. The backbone is also referred to as the bus. When a node wants to send a message over the network it puts a message over the network.
344 Rigid Metal Conduit. What is the cable type used in the backbone of a bus topology. This type of network topology makes it easier to connect a computer and its peripherals to a linear bus.
When one terminator is missing connectivity comes to a stop. Type ALS cable Type CS cable mineral-insulated metal-sheathed cable or Type MC cable. The cable which is used as backbone cable is a coaxial cable.
Bus topology is a network topology type that connects all devices in a line. Learn More About Our Company. Shop 7000 Products Now.
Los Angeles CA Distributor 10 - 249 Mil 1952 10-49. 342 Intermediate Metal Conduit.

Explanation Of Network Topology Types

Comments
Post a Comment